What are Ovarian Cysts? Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
Table Of Content
- The bloodied and bruised image that puts a human face on the High Court fallout
- Did You Know Dermoid Cysts Can Have Hair, Skin, and TEETH?
- Cysts caused by ovulation
- What happens if an ovarian cyst ruptures?
- How do healthcare providers treat teratomas?
- Ovarian cysts
- How is a dermoid cyst treated?
- Common ovarian cyst signs
Cysts that cause symptoms should, however, be removed surgically. If malignancy is suspected, surgical removal will be recommended. If people experience symptoms of any complications, they should seek prompt medical attention. This is because they develop during the development of an embryo. They most commonly affect the ovary on the right side, but in 12% of cases, they can develop on both ovaries. According to a 2022 article, the size of these cysts can vary from very small, to larger than 39 centimeters (cm).
The bloodied and bruised image that puts a human face on the High Court fallout
But, unlike MCTs, the cells are haphazard and not fully differentiated. Your provider may recommend surgery to remove your cyst if they're concerned that it could rupture or twist your ovary. If it doesn’t cause immediate concern, they may monitor it instead. Tissue from sweat glands can form inside of the cyst, too. These glands secrete an oily fluid called sebum that causes your cyst to grow.

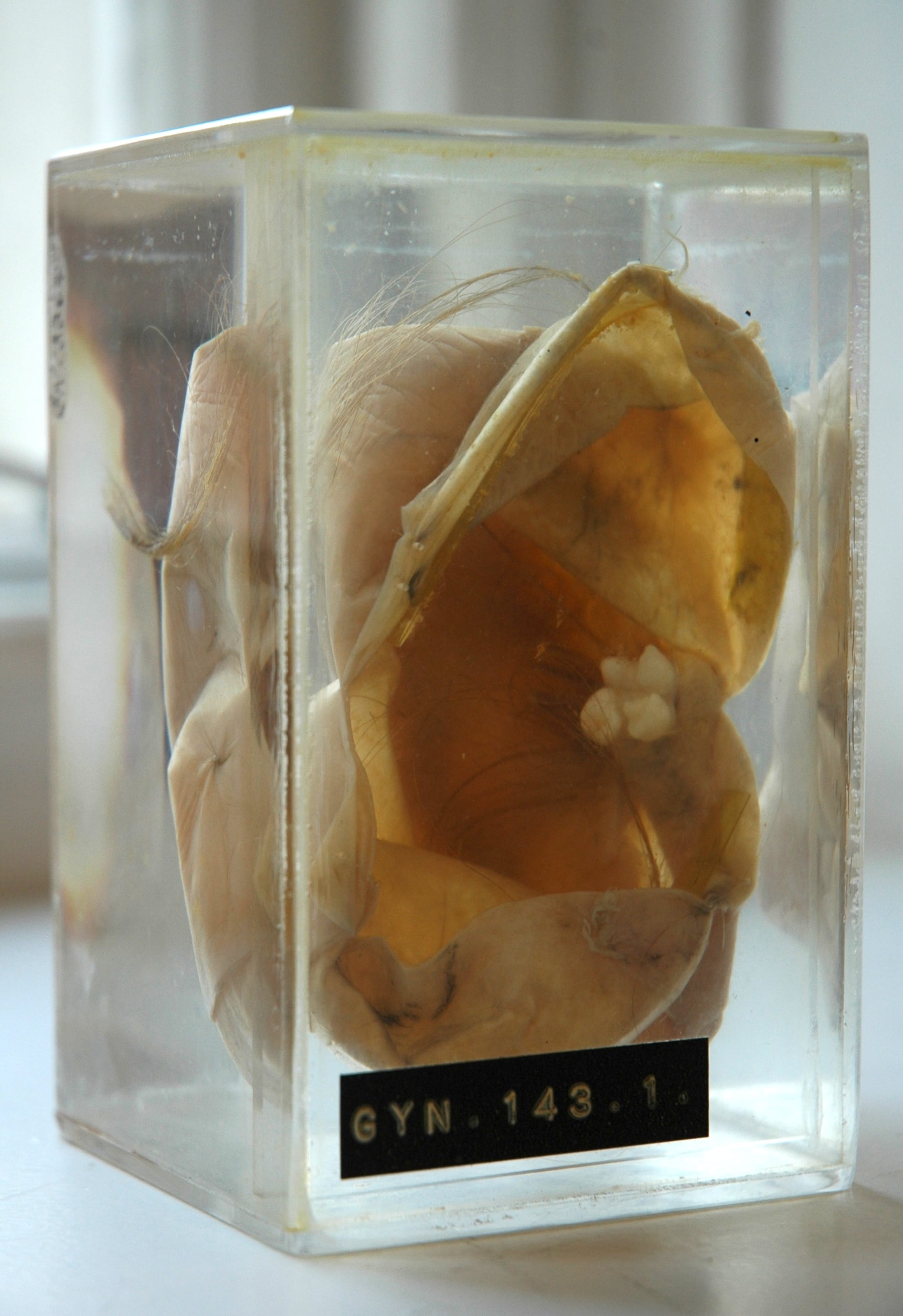
Did You Know Dermoid Cysts Can Have Hair, Skin, and TEETH?
It’s not uncommon, for instance, to learn during a pregnancy ultrasound that you have this type of cyst. A 2016 article states that ovarian dermoid cysts account for 70% of all benign ovarian masses affecting females in their reproductive years. They also account for 20% of benign ovarian masses in postmenopausal people. The rarest type of teratoma tumor, a fetiform teratoma occurs in about 1 out of every 500,000 people. It’s a type of dermoid cyst that consists of living tissue and often resembles a malformed fetus.
Cysts caused by ovulation
In rare cases, a dermoid cyst extends into a structure deeper than skin, such as a facial cavity or an orbit. Some doctors recommend a CT scan or other imaging studies for these cases. This decision depends on the doctor’s suspicion of a deep-level cyst and after a determination of risk versus benefit.
Also known as teratomas, these cysts are typically benign (non-cancerous) tumors that develop from the primary oocytes, or the cells that give rise to eggs. A primary oocyte is a totipotent cell, meaning it can become any other type of cell. For this reason, these cysts may contain hair, skin, teeth, bone or fat in them, because they form from embryonic cells. The most common type of ovarian cyst is known as a functional ovarian cyst. Functional cysts are often harmless and painless, and typically go away after two or three menstrual cycles.
Although there is no way to fully prevent an ovarian cyst, regular pelvic exams will help your doctor identify any abnormalities as early as possible. Your primary care doctor, gynecologic oncologist, or an obstetrics and gynecology (OB/GYN) doctor may diagnose if you have one or more ovarian cysts. For postmenopausal women, pathological cysts (ovarian cysts that are not related to menstruation) increase the likelihood of developing an ovarian tumor. Your ovaries grow cyst-like structures called follicles every month to produce hormones and release the egg.
Ovarian cysts
The cyst's response to treatment is also a significant prognostic factor. If the dermoid cyst is larger than 5 cm–6 cm, an oophorectomy (surgical removal of an ovary) may be recommended. This is likely to be considered if the cyst distorts the ovary's structure. The ovaries also manufacture the hormones estrogen and progesterone. These hormones regulate ovulation (release of the egg from the ovary) and the menstrual cycle. In most cases, these tumors don’t spread like aggressive cancers.
How is a dermoid cyst treated?
Nearly all teratomas require removal when discovered. Even if they aren’t cancerous, they can still grow or rupture, leading to other issues. With the development of imaging technology, healthcare providers can sometimes diagnose a teratoma during pregnancy. Another type of cyst occurs after an egg has been released from a follicle. This type of cyst may contain a small amount of blood.
Common ovarian cyst signs
Studies which encourage women to seek care for possible ovarian cancer symptoms have not shown any benefit. Unfortunately, we do not have any proven means of screening for ovarian cancer. Functional ovarian cysts often do not need treatment.
An ovarian dermoid cyst is a germ cell tumor that develops on the ovaries. Although they are benign, they can become cancerous in rare circumstances. In the early stages of every menstrual cycle, the ovaries normally develop small cyst-like structures called follicles.
Your Health: Brain-on-fire disease - WILX
Your Health: Brain-on-fire disease.
Posted: Fri, 12 May 2023 07:00:00 GMT [source]
People may also refer to them as mature cystic teratomas. Head and neck teratoma tumors make up less than 6% of all teratomas. But you may also develop specific additional symptoms based on the location of the teratoma tumor. A fetiform teratoma resembles a parasitic twin (fetus in fetu). Fetus in fetu only occurs in twins who both share the same placenta and have their own sac of amniotic fluid.
Ovarian Tumors with Brain Tissue, Teeth or Hair (Not Unheard Of) - American Council on Science and Health
Ovarian Tumors with Brain Tissue, Teeth or Hair (Not Unheard Of).
Posted: Sat, 07 Jan 2017 08:00:00 GMT [source]
Dermoid cysts account for around 70 per cent of benign ovarian tumours in those under age 30, and half of all children’s tumours. It’s unclear just how often these tumours are appearing, since most of the time they are only discovered accidentally, during other imaging. Observation or watchful waiting may be the preferred course. If a dermoid ovarian cyst is larger or producing symptoms, it may be removed surgically. If a dermoid cyst in an ovary is malignant, your prognosis will be determined by the cyst's growth pattern, invasiveness, and stage.
Since a twisted ovary can reduce or stop blood flow, the sooner you get medical attention, the better chance there is for your ovary to be saved. Changes in the follicle of the ovary after an egg has been released can cause the egg's escape opening to seal off. Fluid builds up inside the follicle, and a corpus luteum cyst develops. If the follicle does not release its egg, and instead continues to grow and fills with fluid, a follicular cyst can form.
You may be told to watch your symptoms over time (“watchful waiting”). An ovarian cyst will often go away with no treatment in a few weeks or months. Dermoid cysts are basically encapsulations of wayward cells that ended up in the wrong spot and kept on growing, she explains. You may feel sick to your stomach or throw up if a cyst moves your ovary out of place (ovarian torsion) or breaks open.
Comments
Post a Comment